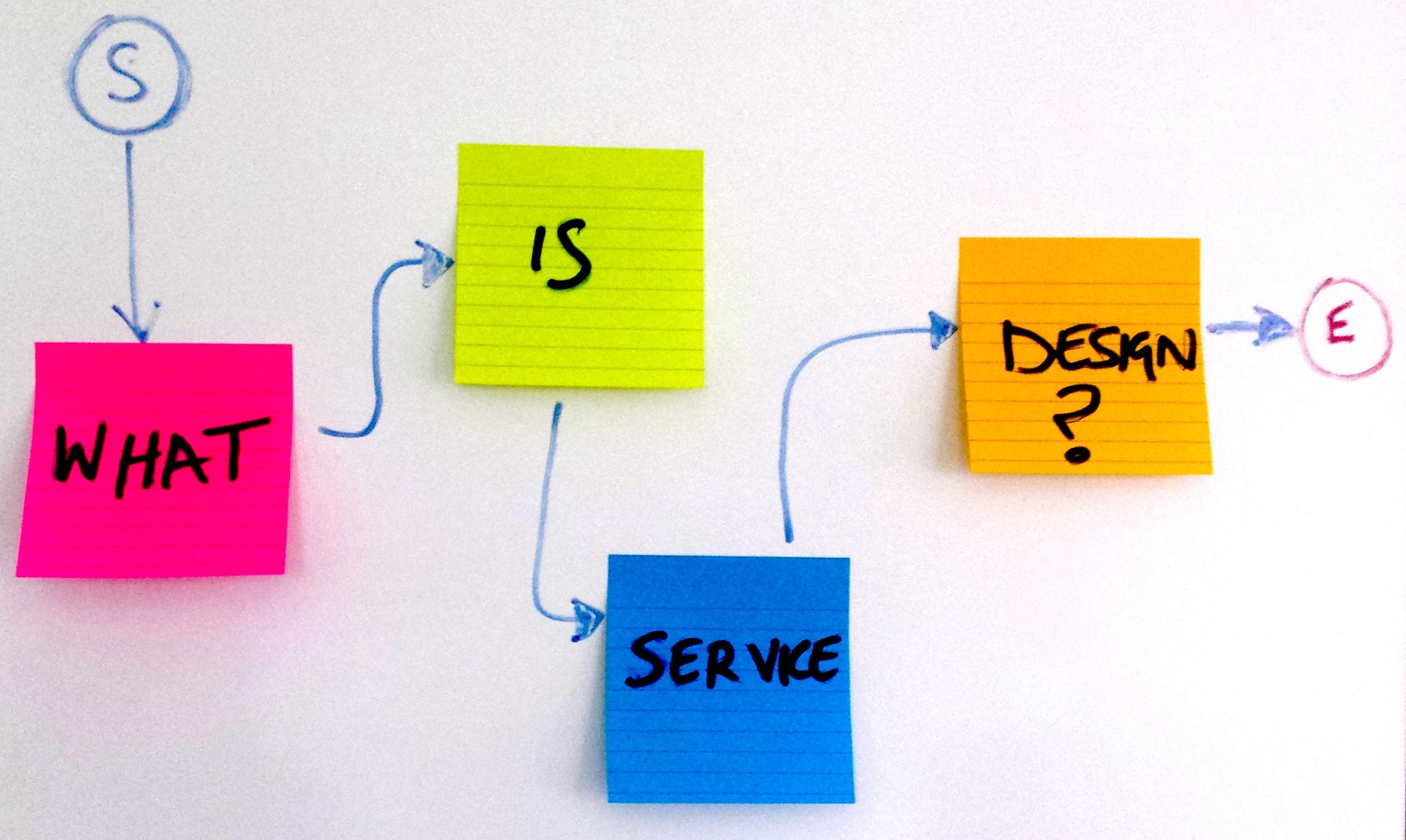
Utilising Soft Systems Methodology (SSM) to solve complex business design problems
Addressing Complexity with a Soft Systems Approach......
Checkland's Soft Systems Methodology (SSM) is a systems thinking approach for understanding and addressing complex business problems. It was developed by Peter Checkland in the 1960s and has since been widely used in a variety of industries and contexts.
The main concepts of SSM include:
- Systems: A system is a set of interrelated elements that work together to achieve a common purpose. In SSM, the focus is on understanding the complex systems that underlie business problems, rather than on individual components.
- Root definitions: Root definitions are statements that describe the purpose of a system in terms of the outcomes it is intended to achieve. Root definitions help to clarify the goals and objectives of a system, as well as the values and assumptions underlying them.
- CATWOE: CATWOE is a mnemonic that stands for the six components of a root definition: Customers, Actors, Transformation process, Weltanschauung (worldview), Owner, and Environmental constraints.
- Rich pictures: A rich picture is a visual representation of a complex system, highlighting the relationships and interactions among the various elements of the system. Rich pictures help to identify the key issues and stakeholders in a system, as well as the underlying structures and processes.
The sequence of SSM consists of the following steps:
- Identify the problem: The first step in SSM is to identify the problem or challenge that needs to be addressed. This may involve gathering data and conducting stakeholder interviews to gain a deeper understanding of the problem and its context.
- Develop a rich picture: A rich picture is then created to depict the complex system that underlies the problem. This can be done through visual mapping or diagramming techniques, such as mind mapping or causal loop diagrams.
- Construct root definition(s): The next step is to construct root definitions for the problem, using the CATWOE framework. This helps to clarify the purpose and goals of the system, as well as the values and assumptions underlying them.
- Analyze the system: The rich picture is then used to analyze the system and identify the key issues, stakeholders, and dynamics that are contributing to the problem.
- Generate alternatives: Based on the analysis of the system, a range of alternative solutions or interventions is then generated.
- Evaluate and select: The alternatives are then evaluated based on their feasibility, acceptability, and effectiveness, and the most promising solution is selected for implementation.
- Implement and review: The selected solution is then implemented, and the results are monitored and reviewed to assess its impact and effectiveness.
Overall, SSM is a flexible and iterative approach that helps organizations to understand and address complex business problems in a holistic and systems-oriented way.
It is particularly useful for tackling problems that are vague, ambiguous, or difficult to define, and that involve multiple stakeholders and competing interests.
Contact info@witwam.com to discuss your business problem and how we might help solve it.
Thoughts on Service Design and Operating Models